Describe the Structure of a Molecule of Hemoglobin
If all of the monomers in a protein are. Calculate the net charge on a molecule at any pH.

Hemoglobin An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
A part of DNA- genes are made up of A T G and C nucleotides.
. A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. Each hemoglobin molecule binds four oxygen molecules so that each red blood cell carries one billion molecules of oxygen. Chemical also can be an adjective to describe properties of materials that are the result of various reactions between different compounds.
The 3 following numbers eg 14699 61369 62050 for the very first atom are the xyz coordinates of the atom. Its chemical formula is H 2 O. The terms dominant and recessive describe the inheritance patterns of certain traits.
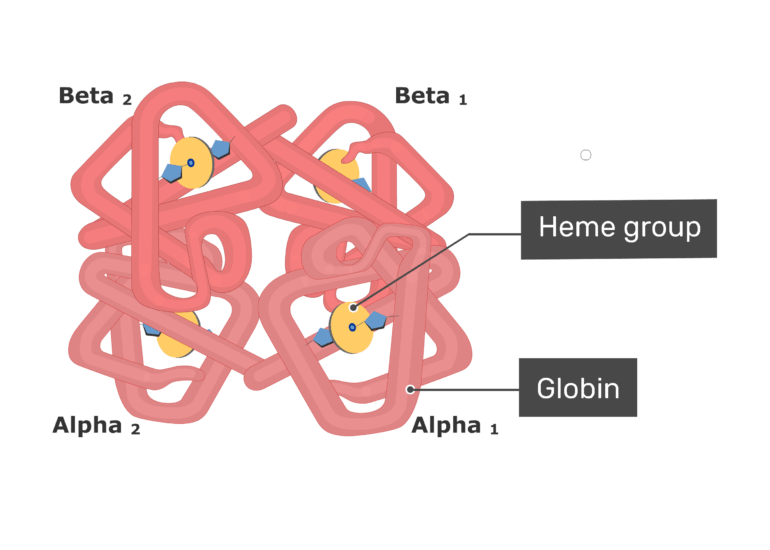
There are approximately 25 trillion red blood cells in the five liters of blood in the human body which could carry up to 25 sextillion 25 10. Each amino acid contains a central carbon a hydrogen a carboxyl group an amino group and a variable R group. Hemoglobin has a quaternary structure.
But what do they really mean. The secondary structure of chymotrypsin consists of several antiparallel β pleated sheet regions and a little α helical structure. Characterize molecular forces between antibody and antigen.
Usually proteins that have greater than 50000 molecular weight have two or more noncovalently-linked monomers. The folded structure is stabilized by noncovalent interactions between different parts of the polypeptide chain. By convention the letters ose at the end of a biochemical name flags a molecule as a sugar.
Small compartments called vesicles carry materials throughout the cell. HOW VESICLES TRANSPORT CARGO. But he was unable to describe the chemical structure of it.
As in myoglobin each subunit is linked covalently to a molecule of heme. Explain how the structure of different segments of the respiratory airways reflect the functional roles that these airways play in air movement and gas exchange. Electrically charged hydrophilic side chains polar but uncharged side chains nonpolar hydrophobic side chains.
It is a term used to describe proteins consists of multiple polypeptide molecules. Understand why solutions of weak acids resist pH changes. It is called quaternary structure because the arrangement of monomers in three-dimensional.
Because there are two different subunits hemoglobin exhibits heteroquaternary structure. Understand the relationship between the structure and acidity of an acid. Proteins are polymers of amino acids.
In 1953 James Watson and F Crick defined the chemical structure of the DNA viz gene. Fructose and some other less well known sugars are ketones. There are 141 and 146 amino acids in the α and β chains of hemoglobin respectively.
Compare the two ways for organisms to pass genetic information to their offspring. The hemoglobin proteins possess heterogeneous quaternary structure because it in the form of two catalytic trimers and three regulatory dimers. As mentioned above they describe the position of each atom in an.
Since then technology has given us an increasingly complex view of the basic unit of life. There are two α-chains each with 141 amino acids and two β-chains each with 146 amino acids. Find out about autosomal x.
Of these sugars all but one fructose exists as an aldehyde. Distinguish the trachea bronchi terminal bronchioles bronchioles alveolar ducts alveolar sacs and alveoli based on key structural. Hemoglobins quaternary structure is the package of its monomeric subunits.
Thus hemoglobin binds four O 2 molecules. Figure 2148 shows the structure of these sugars. Describe the process of antibody production by B-cells.
In 1665 Robert Hooke coined the term cell to describe the structures he could see in cork with some of the first microscopes. A DNA Molecule Consists of Two Complementary Chains of Nucleotides. In cases when the structure consists of several polypeptide chains eg.
DNA analysis can help build the family tree. Each polypeptide molecule is called monomer. The 4 Types of DNA and Molecular Genealogy.
A process that involves the rearrangement of the molecules or structure of a substance as opposed to a change in physical form as from a solid to a gas. Describe the structure and function proteins. It consists of two pairs of different proteins designated the α and β chains.
The amino acids with hydrophobic side chains tend to cluster in the interior of the molecule and local hydrogen-bond interactions between neighboring peptide bonds give rise to α helices and β sheets. Based on higher level of structure. Define the terms antigen epitope and hapten.
Describe the changes in the type of epithelium throughout the respiratory system. Genes are actually DNA strands thus are made up of the nucleotide chain. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain or a DNA strandHydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together As we saw in Chapter 2 Panel 2-6.
Hemoglobin is composed of four monomers. As in the tetramers of hemoglobin and Pyruvate kinase discussed earlier each chain will get its own identifier like A B C etc. The R group specifies which class of amino acids it belongs to.
Thus there are glucose galactose sucrose and many other -oses. Hemoglobin is packed into red blood cells at a rate of about 250 million molecules of hemoglobin per cell. The chemical structure of a gene comprises nucleotides.
A molecule of chymotrypsin consists of 3 short polypeptide chains of 13 131 and 97 amino acid residues respectively supported by two interchain disulfide bonds.
What Is The Molecular Structure Of Hemoglobin Quora

Hemoglobin Structure Function Impairment Study Com
What Is The Structure Of Hemoglobin And How Is Oxygen Bound To It Quora
Comments
Post a Comment